June 3, 2021
World-first artefact dating method shows humans have lived in the shadow of the Himalayas for more than 5,000 years
A new technique suitable for dating ancient stone tools has revealed the presence of early humans on the Tibetan Plateau
Few parts of the world would seem as inhospitable to humans as the highlands of the Tibetan Plateau, near the Himalayas. Archaeologists have long wondered when, where and how our ancestors began to explore and occupy these landscapes.
But evidence of early human presence on the plateau has been scarce — and dating the few remaining traces has proven an ongoing challenge.
Using a recently developed dating technique, our research team has now produced the first solid evidence for human presence on the central-southern Tibetan Plateau more than 5,000 years ago. Our findings are published today in Science Advances.

The challenge of dating surface artefact scatter
The dry highlands of Tibet are considered to be among the last areas on Earth to have been settled by humans. The high altitude of the region, in the shadow of Himalayan peaks more than eight kilometres high, makes for extreme conditions.
The question of where and when the peopling of this remote region occurred has been debated among archaeologists. Many studies have come from research conducted at open-air locations, with abundant evidence of stone tool use or manufacture, such as rock flakes found on the ground.
These sites are referred to as “lithic artefact scatters”. They are among the most commonly preserved archaeological sites in the world, and hold potential to reconstruct human settlement patterns and explore various aspects of past human behaviour.
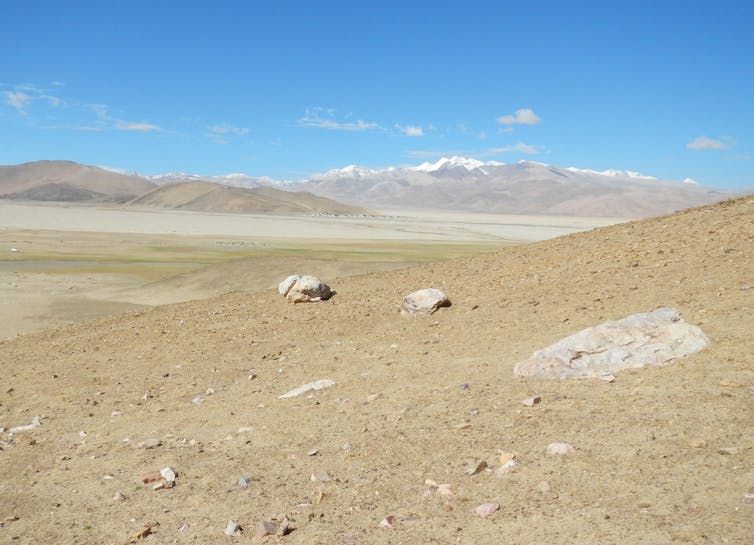

Yet it has been extremely difficult to interpret the archaeological significance and ages of these sites unambiguously. Most artefacts are made from stone, which makes it difficult to determine when the tools were manufactured, or if they were moved after being discarded.
Artefacts on the surface are prone to erosion, and movement by wind and water, over hundreds or even thousands of years since humans first produced them. Consequently, they’re often found “out of context”, so a clear relationship can’t be drawn between them and their immediate surroundings.
Developing new techniques
To overcome this limitation, our team spent the past several years in the Innsbruck OSL (optically-stimulated luminescence) dating laboratory in Austria led by Michael Meyer at the University of Innsbruck, developing a new technique suitable for dating ancient stone tools.

OSL dating has become one of the main dating methods in archaeology and the earth sciences. It’s based on the accumulation of energy in the crystal structure of sand grains.
When grains are shielded from daylight, such as when they’re buried, their crystal accumulates energy due to low-level radiation from surrounding rocks and sediment.
This can then be measured in the laboratory, through controlled exposure to blue and green light, which releases the energy as a “luminescence signal”. The longer the grains have been buried, the more luminescence we will measure from them.
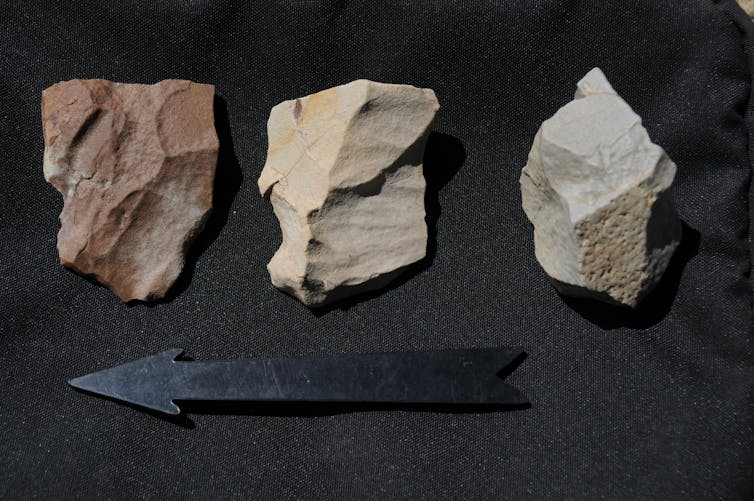
Instead of looking at sand for our research, we used an approach called “rock surface burial dating”. It’s the first ever approach to focus on the signal stored beneath the surface of rock artefacts at a scatter site.
The luminescence signal built up within a rock is almost infinitely high, due to the extremely long time that has passed since the rock was formed by geological processes.
However, once a rock surface is exposed to daylight, such as when an artefact is first produced and used, the luminescence signal is erased at the surface and just beneath (but not at the centre). The erasure of the signal is strongest at the surface and tapers off towards the centre of the artefact.
When the artefact is thrown away and becomes shielded from daylight — either from beneath, or from being covered by sediment — the signal starts to build again.
This leads to varying levels of signal intensity found at different depths beneath the artefact’s surface. We can measure this signal distribution to determine the overall age and history of a stone artefact.

5,000 years in the shadow of Mount Everest
The large potential of this new way of using OSL had been shown in previous archaeological and geological contexts, but hadn’t been rigorously tested on artefact scatter sites.
Accompanied by experienced high-altitude archaeologist Mark Aldenderfer from the University of California at Merced, and supported by mineralogist Peter Tropper from Innsbruck, we set out to test the suitability of this promising method at the lithic artefact scatter site of Su-re, in southern Tibet.
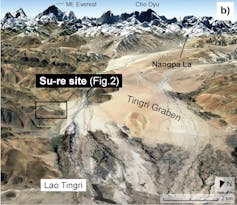
At an elevation of 4,450 metres, in a large valley descending from the highest peaks in the world – Mount Everest and Cho’Oyu — Su-re had been known for decades for its dense accumulation of diverse surface artefacts. This suggested a long history of site use by humans. But how long?
Using our dating approach, we dated the oldest artefacts found at the Su-re site as being between 5,200 and 5,500 years old. These tools were likely related to quarrying activities at the site.
While some older sites have been discovered in central and southeastern Tibet, our dataset has made Su-re the oldest securely dated site in the central-southern Tibetan Plateau near the high Himalaya.
This finding is particularly exciting considering the proximity of Su-re to the “Nangpa La” mountain pass. This pass has historically connected local Tibetans in the highlands with Nepali Sherpas in the Himalayan valleys and lowlands.
Our new approach to analysing surface artefacts can be considered the beginning of a road to new archaeological perspectives. In the future it could help uncover the secrets of lithic artefact sites around the world.
Jan-Hendrik May, Senior Lecturer, School of Geography, Earth & Atmospheric Sciences, Faculty of Science, The University of Melbourne and Luke Gliganic, Research Fellow, School of Earth, Atmospheric and Life Sciences (SEALS), University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license.
UOW academics exercise academic freedom by providing expert commentary, opinion and analysis on a range of ongoing social issues and current affairs. This expert commentary reflects the views of those individual academics and does not necessarily reflect the views or policy positions of the University of Wollongong.
