Dynamic multimode vifs can detect not only the loss of link status (as do static multimode vifs), but also a loss of data flow. This feature makes dynamic multimode vifs compatible with high-availability environments. The dynamic multimode vif implementation in Data ONTAP is in compliance with IEEE 802.3ad (dynamic), also known as LACP.
Dynamic multimode vifs have some special requirements. They include:
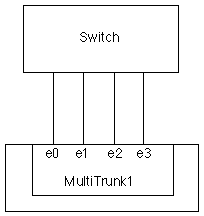
In a multimode vif, all interfaces in the vif are active and share a single MAC address. This logical aggregation of interfaces provides higher throughput than a single-mode vif. Static multimode vifs can recover from a failure of up to (n-1) interfaces, where n is the total number of interfaces that form the vif.
A multimode vif requires a switch that supports link aggregation over multiple switch ports. The switch is configured so that all ports to which links of a vif are connected are part of a single logical port. For information about configuring the switch, see your switch vendor's documentation. Some switches might not support link aggregation of ports configured for jumbo frames. For more information, see your switch vendor's documentation.
Several load-balancing options are available to distribute traffic among the interfaces of a multimode vif.
Data ONTAP is only responsible for distributing outbound traffic and does not have control over how inbound packet arrive because each end of an aggregate is responsible for controlling the distribution of its outbound traffic.
The following figure is an example of a multi-mode vif. Interfaces e0, e1, e2, and e3 are part of the MultiTrunk1 multimode vif. All four interfaces in the MultiTrunk1 multimode vif are active.